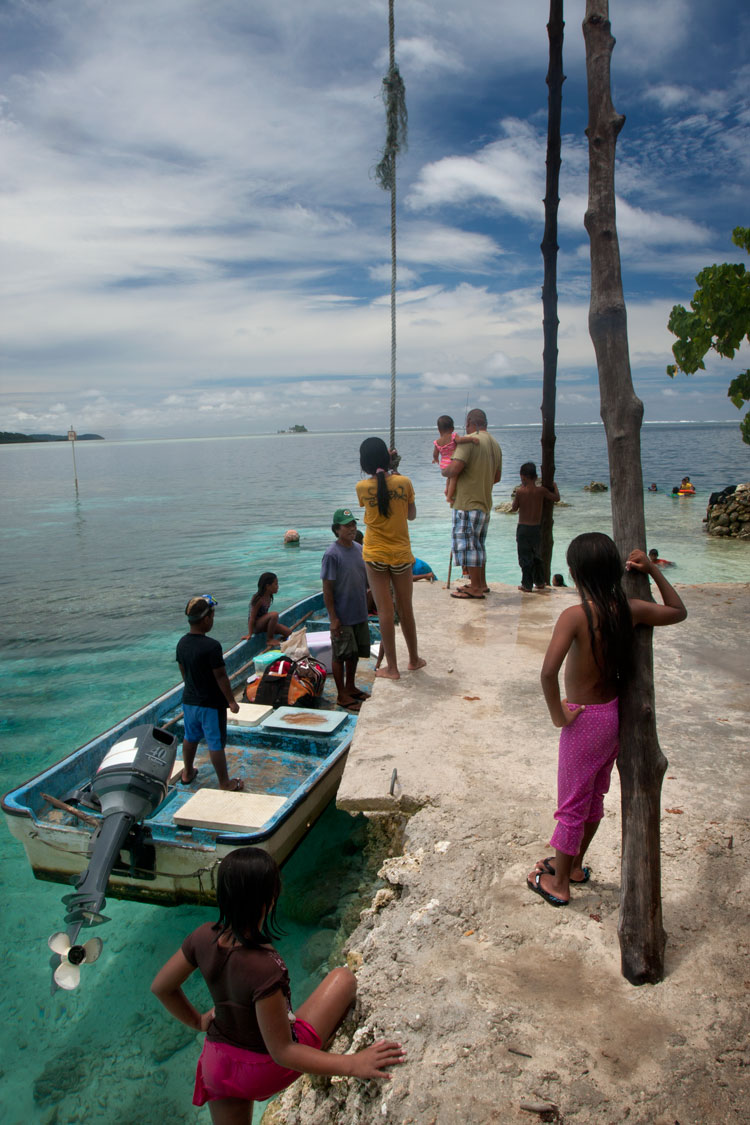Dauen Sapwalap / Senipehn Mangrove Reserve
Dauen Sapwalap is the largest drainage in Madolenihmw, a wide, meandering channel that cuts through the mangrove forests from Kitamw and eventually empties into Madolenihmw Bay. Although the Lehdau River (Pillapen Lehdau) is probably the largest contributor to this major estuary, the two are not synonymous; the channel is also fed by three other watercourses, including the Kitamw Stream (Pilen Kitamw), Pwadapwad Stream (Pilen Pwadapwad), and River of Sekere Riau (Pillapen Sekere Riau). According to legend, a powerful demi-god named Lapongo — the same character involved in the story of Takaiuh peak — dug out the channel with his penis. The matriarch of the Lasialap Clan — a great eel responsible for the creation of Lipwentiak in Kitti and whose tail formed the great mountain in Nett, Pohnlehr — was also said to have dwelt in this channel for many years, terrorizing the local inhabitants.
During the 1889-1890 wars between the Spanish and Pohnpeians, which began in Ohwa and concluded in Kitamw, two contingents of Spanish troops were dispatched at the mouth of Dauen Sapwalap and attempted to move up both banks of the Pillapen Lehdau (Lehdau River) to reach a small half-finished fort built on a low hill by the Pohnpeian fighters. The first group of soldiers got terribly lost in the tangled forests and happened upon the fort only by mere chance. The second group was forced off-route by a seemingly supernatural flood and also ended up lost, camping overnight at Elieliwi before joining the fray. The assault cost the Spanish 21 men, and in the end the Pohnpeians merely withdrew and yielded a position that had meant little to them from the beginning.
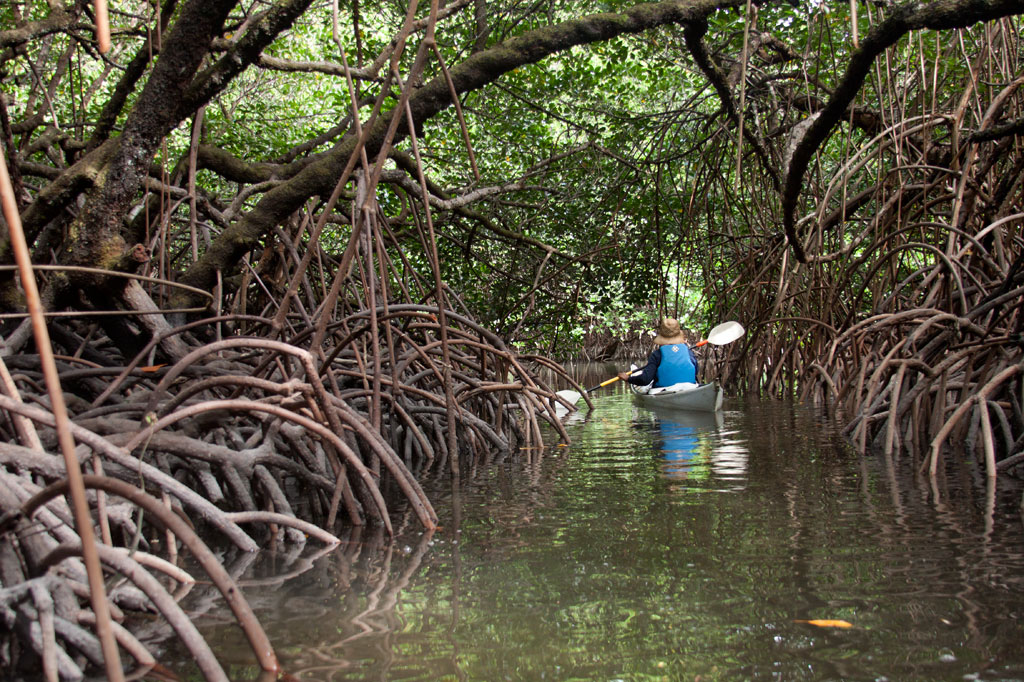
In the last decade, the estuary became part of the Senipehn Mangrove Forest Reserve and afforded some environmental protections; tree-cutting, fishing, and gathering of other natural resources in the area is prohibited in most circumstances. Paddlers can explore the 2.6 km (1.62 mi) primary channel and its side passages by launching near the Lehdau River bridge, at the end of the road near Tahio, at the Madolenihmw “Ice Dock”, or at the MERIP boathouse.
- Entering the mangrove reserve requires a permit. Visit our MPA page for details.
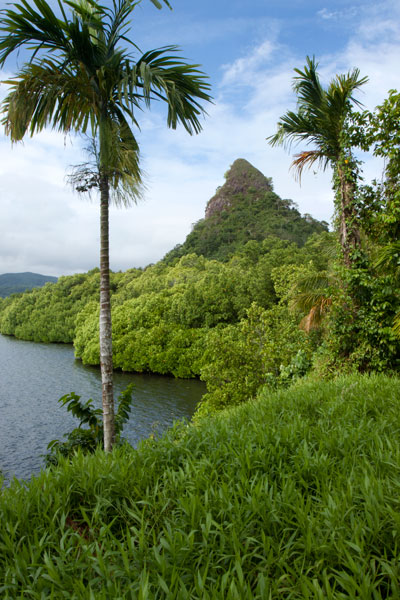

Takaiuh Peak
While Sokehs Rock is the stand-out natural feature in the north, in Madolenihmw that title certainly goes to Takaiuh (“standing rock”), a majestic conical hill-island on the north side of the bay. Westerners called this feature “Sugarloaf” after the molded cones of sugar that were popular in Western Europe as early as 1470, but the local name and its story are much more interesting (see Madolenihmw Bay Area page for more).
Paddlers can get right up close to the iconic hill for a view from the water that is better than from anywhere on land. There’s also good fun to be had noodling around in the mangrove forests on the eastern shore (at high tide). A sweet spot to stop for a picnic lunch is the top of an exposed rocky rise 0.36 km (0.22 mi) northwest of the peak (no mangroves skirt this bit of the shore).
Pahn Dieinuh
Pahn Dieinuh, the southern point of the Dolopwail peninsula, is significant historically for the 1836 conflict that began there between the visiting British whaleship Falcon and two rival Pohnpeian chiefs — Luhk en Kesik ( the Nahnmwarki) and the Wasai, the first and second ranking men in the royal line, respectively. Things got ugly when the Nahnmwarki made a move to seize the ship and its cargo. When the ship attempted to flee, it ran up on the reef. The cargo was transferred to Nahpali Island and then stolen a month later by the Nahnmwarki‘s brother, Nahnawa. A battle ensued on Nahpali between Nahnawa‘s party and the whalers, ending in the deaths of the ship’s captain and three other sailors. The Wasai, who had been challenging the Nahnmwarki‘s authority for some time, seized this opportunity to rid the land of his enemy by joining the crews of other whaleships in hunting down both Nahnawa and the Nahnmwarki. Fighting continued for several days until the Nahnmwarki was shot and Nahnawa captured and hanged from the yardarm of the whaleship Lambton. Both bodies were buried at Pahn Dieinuh, and the Wasai assumed the position of the Nahnmwarki. There isn’t much of anything to see at Pahn Dieinuh now, but it’s a good spot for a break mid-route. The closest launch points are MERIP boathouse, the “Ice Dock”, and the Metipw launch.
Mwudokolos Island
In addition to the seven islands (Nahpali, Dekemwahu, Na, Dehketik, Nahkapw, Nahnningi, and Mall) found around Temwen, there are three small islands to the north that shouldn’t be missed. The first of these — Mwudokolos — is found a half-kilometer (0.33 mi) northeast of Metipw and easily accessed from the coral-dredged causeway/dock found there (ask at the nearest house for permission to launch). Archaeologist Arthur Saxe believed that the island was tied to Nan Madol in some way and that it might even be a man-made island, but Japanese archaeologists working on the island in recent years have found no hard evidence to support that idea. They did discover prehistoric stone structures and a house platform that dates to the Nahnmwarki Period of Nan Madol (post-1700). Glass beads, sherds, and clay pipes were also found, suggesting that Mwudokolos was occupied by foreign traders in the late 1800s. The island is privately owned, but unoccupied.
- To obtain permission for day visits or overnight stays, call Sesuko Hadley at +691.320.2540.
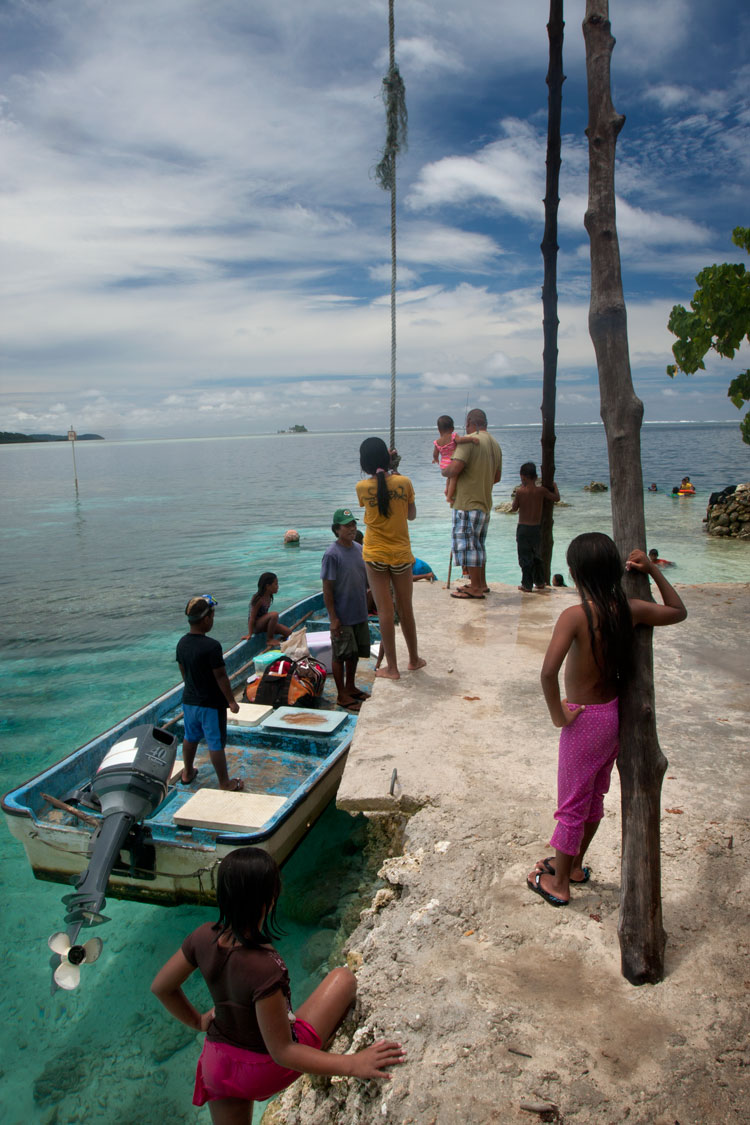
Dahu Reirei Island
From Mwudokolos, paddlers can continue 1.8 km (1.13 mi) further north through the easternmost of two dredged reef channels to reach Dahu Reirei (“long channel”), a narrow, man-made islet with huts for picnickers and campers and lots of pleasant swimming and snorkeling. When we say this island is narrow, we mean narrow (10 meters wide). Unless you like being crammed together elbow-to-elbow, avoid the place on weekends and holidays. It’s also not a place to be on intensely hot days (there are no trees large enough to provide shade) or during bad weather (the island is hardly a meter above sea level at high tide). On partly-cloudy weekdays, however, it can be heavenly. The surrounding water is generally crystal-clear and the reefs, which consist mainly of varieties of staghorn coral, are surprisingly healthy and relatively well-populated with reef fish. Small thatched huts along the length of the strip can be rented for the day or overnight.
- To make reservations for day visits or overnight stays and to arrange boat transport, call Joseph Helgenberger at +691.320.2229.
Lepin Dau (“Channel Island”)
The final island covered in this sector (it’s just off the edge of the Central Madolenihmw map, but appears on the U & Northern Madolenihmw map) is claimed by the same family as Dahu Reirei and has no official name, but as it lies adjacent to the primary channel every boat in the area uses to go from Areu and Ohwa to Madolenihmw Bay, it’s known as Lepin Dau or “Channel Island.” This island is larger and higher than Dahu Reirei and has some welcoming tree-cover (mostly pandanus). The channel on the west side is a nice spot to snorkel at slack tide, but at other times, the current can be so strong that snorkelers and swimmers run a strong risk of being swept away. A better spot for snorkeling is in the blue holes around the southeast side — well out of the path of the current. Here you can find beautiful coral grottoes, huge schools of needlefish, barracuda, cuttlefish, trumpetfish, angelfish, and parrotfish, an odd seasnake (the latter are venomous, but so passive that they pose little danger to snorkelers), and from time to time even eagle rays and small green turtles. It’s a fantastic picnic destination for paddlers.
- You don’t really need to get permission to make day visits to “Channel Island,” but overnighters should call Joseph Helgenberger at +691.320.2229.
Nanwap Marine Protected Area
The reefs on the north side of Kepidauen Deleur make up the Nanwap Marine Protected Area (MPA), a marine reserve with excellent snorkeling and diving. The best place to snorkel is about 1.3 km east of Metipw in a protected reef hole, but watch for strong currents.
Paddling Distances Around Central Madolenihmw
| Starting |
|
Ending |
Distance (km) |
Distance (mi) |
| “Ice Dock” |
—- |
Tahio* |
3.12 km |
1.94 mi |
| “Ice Dock” |
—- |
Sekeren Senipehn |
2.5 km |
1.6 mi |
| Sekeren Senipehn |
—- |
Dauen Wetiak |
1.7 km |
1.0 mi |
| Dauen Wetiak |
—- |
Dauen Sapwalap |
1.3 km |
0.8 mi |
| Dauen Sapwalap |
—- |
Pilen Kitamw (Kitamw Stream) Bridge |
2.6 km |
1.6 mi |
| “Ice Dock” |
—- |
Takaiuh Shore* |
2.45 km |
1.5 mi |
| “Ice Dock” |
—- |
Pahn Dieinuh* |
2.6 km |
1.62 mi |
| Takaiuh Shore* |
—- |
Diadi |
3.44 km |
2.1 mi |
| Japanese Wharf, Temwen Is. |
—- |
Diadi |
0.99 km |
0.61 mi |
| MERIP* |
—- |
Pahn Dieinuh |
2.48 km |
1.54 mi |
| MERIP* |
—- |
Salong Point, Temwen Is. |
2.2 km |
1.4 mi |
| Salong Point, Temwen Is. |
—- |
Japanese Wharf, Temwen Is. |
1.0 km |
0.64 mi |
| Japanese Wharf, Temwen Is. |
—- |
Nahpali Island |
2.63 km |
1.63 mi |
| Nahpali Island |
—- |
Metipw Launch |
2.59 km |
1.61 mi |
| Diadi |
—- |
Metipw Launch |
2.8 km |
1.75 mi |
| Kepidauen Deleur |
—- |
Nanwap Marine Protected Area (MPA) |
1.24 km |
0.77 mi |
| Metipw Launch |
—- |
Mwudokolos Is. Circumnavigation |
1.4 km |
0.9 mi |
| Metipw Launch |
—- |
Dahu Reirei Is. |
1.86 km |
1.2 mi |
| Dahu Reirei Is. |
—- |
“Channel Island” (see U Municipality & Northern Madolenihmw guide) |
1.53 km |
0.95 mi |
| Metipw Launch |
—- |
Pilen Semwei |
2.61 km |
1.62 mi |
*Silted-in reef. This segment may be difficult or impossible to traverse at low tide.
Map Guides >> (Central) Madolenihmw >> Paddling Around Madolenihmw
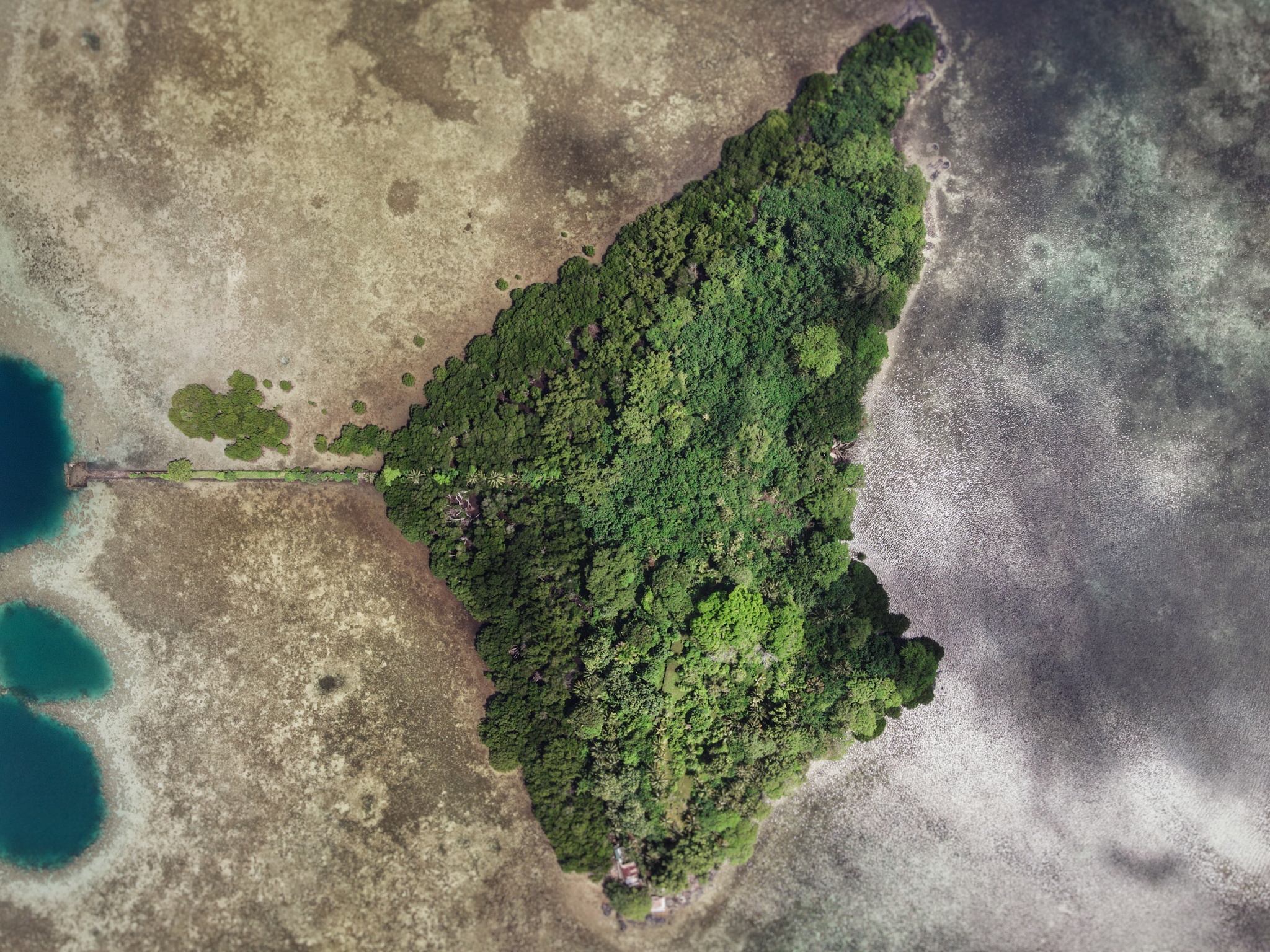
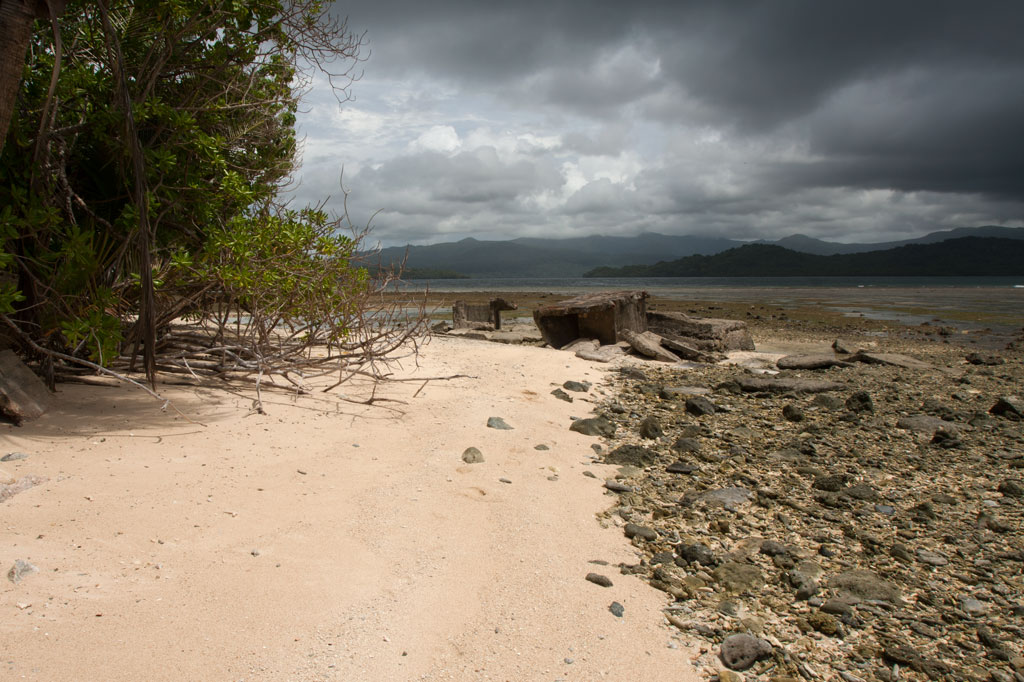
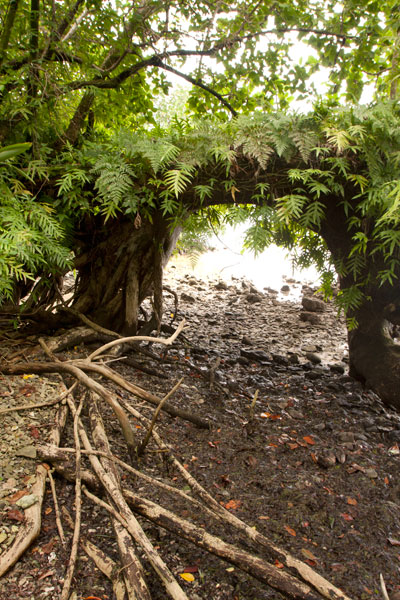
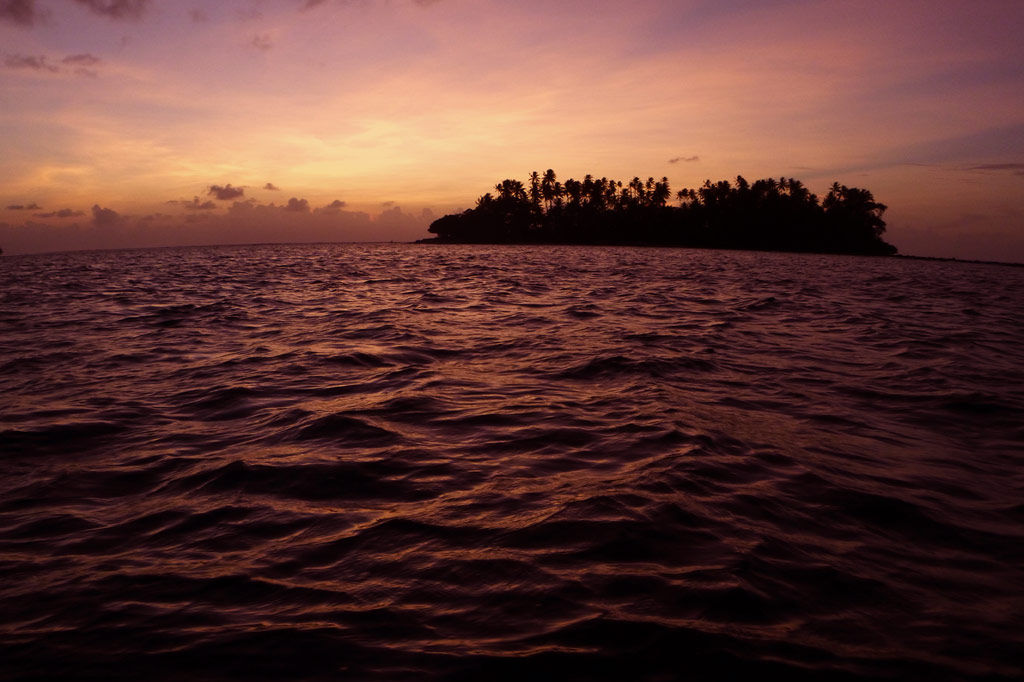












 Further on, stony Salong Point juts north almost to the edge of the channel. Unusual eroded rock formations and a complete lack of mangroves make the place visually unique and worth a look. There’s also a small sea-cave and a portal in the topography that frames conical Takaiuh. Depending on tides and recent rain, the sheltered bay east of the point is sometimes a nice place for a dip, though there isn’t enough coral in the area for snorkeling.
Further on, stony Salong Point juts north almost to the edge of the channel. Unusual eroded rock formations and a complete lack of mangroves make the place visually unique and worth a look. There’s also a small sea-cave and a portal in the topography that frames conical Takaiuh. Depending on tides and recent rain, the sheltered bay east of the point is sometimes a nice place for a dip, though there isn’t enough coral in the area for snorkeling.