Southwest Side

Subterranean Crude Oil Facility (Pahnlenger)
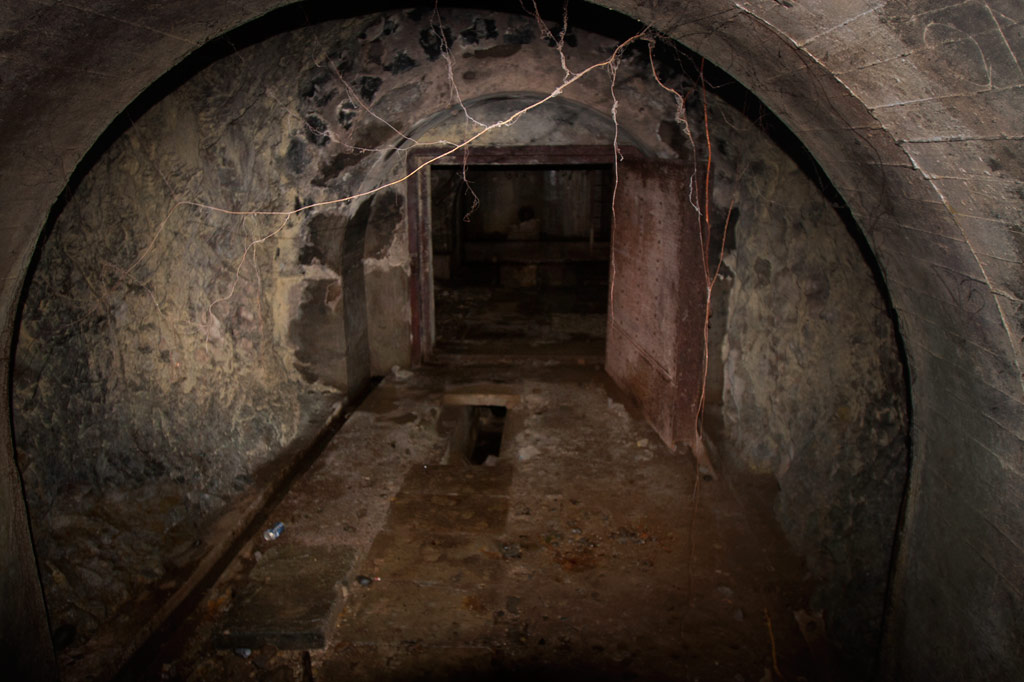
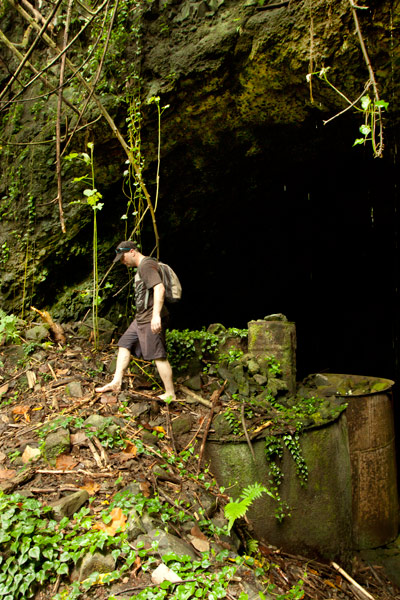
Built beneath Dolen Lenger, the Japanese crude oil storage complex is without question the most impressive of the island’s historical sites. If tight spaces, heights, cobwebs, bats, or the dark make you nervous, this is where you should grab your flashlight and confront your phobias! You don’t want to miss this experience, but do take care where you put your feet and watch out for swiftlets darting about.
The facility is accessed through the first of a trio of steel gates that opens onto a wide rock tunnel lying parallel to the hillside (Gates 2 & 3 are blocked by mud and rock-fall). Steel ladders in alcoves opposite each of the gates run up the wall to concrete lofts from which Japanese personnel could inspect the massive oil tanks. Each tank is 40 meters long and 10 meters wide (131 x 33 ft) with an arched, riveted ceiling and an estimated capacity of 3,300 metric tons. From each loft a second ladder descends 10 meters (33 ft) through a hatch to the floor of the tank. Depending on recent rains, there may between 10 cm and a meter of standing water on the floor, but it’s usually possible to explore without getting too wet. Japanese graffiti on the wall of the first loft reads: “Push forward bravely and strive.” Records seem to indicate that only the third tank was operational. A large diesel engine in front of Tank 3 was probably used to pump the oil in and out. A pipe runs all the way to the coast.

Storage Caves (Pahnaiau)
The four caves carved into the slope of Dolen Lenger were probably intended for use as storage facilities (and also for defense as a last resort), but may not have been completed. Cave 1 is tiny (about 6 meters deep). The other three are grouped together 50 meters (164 ft) to the northwest. Cave 2 is 15 meters deep, 8.5 meters across (49 x 28 ft), and nearly as high with a wide entrance sloping steeply to a soggy floor. If you venture down, be careful of broken glass from bottles that might have been meant for Molotov cocktails (gasoline bombs). Cave 3 is slightly larger and deeper with several terraces. A line of rock-filled barrels at the mouth seems to have been added as protection against a land attack, and the third terrace may have been intended for a machine gun. Cave 4 is the largest with a depth of 28 meters. All of the caves are muddy, often have standing water on their floors, and are occupied by colonies of Caroline Islands swiftlets. The name of the area, Pahnaiau, means “under the banyan tree.”
Concrete Plant Equipment (Pahnaiau)
West of the main path to the caves is a ballast mound with a mango tree on top and a cluster of equipment used in the process of making cement: three concrete mixers, a large Yanmar diesel engine, and the 610 mm gauge rail lines that were used to transport dynamited rock from the cave sites along the hillside. A rock-crusher lies 23 meters (75 feet) southwest of the mixers.
South Side
Oil Tank Complex (Pahnkamal)
This large walled complex originally contained two steel tanks for the storage of crude oil, which was pumped in from the coast. The larger tank, with a 1000-liter capacity, was dismantled in the 1970s by a man who needed steel plates for his ship. He was in the process of taking apart the smaller one, when the government intervened. The existing tank can be entered where the lower panels have been removed. The roof is accessible via a ladder on the inside, leading to a manhole. A courtyard wall surrounds the entire facility (now being used by local residents as a pigpen) and concrete channels lead to a pair of rectangular cisterns (currently piled with coconut husks). Large bomb craters from the American bombardment are found on the northwest and south sides.
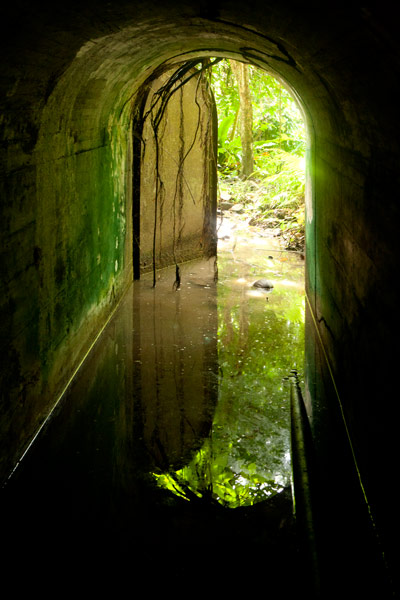

Aviation Fuel Reservoir Tunnel (Pahnkamal)
Northwest of the main path is a subterranean tank that supplied the seaplanes with aviation fuel. A steel door in the hillside opens on a tunnel about 8 meters long (typically flooded with about 20 cm of standing water and silty mud). At the end of the tunnel, the fuel pipes turn to the right and disappear into a concrete wall, behind which the reservoir lies. A ladder runs up to a secondary entrance hatch on the slope, but it is now rusted shut. The Japanese took fuel from this location by truck to the seaplane facility.
East Side
Cisterns & Machines(Nanpeilam)
Footpaths leading toward residences on the eastern coast pass a variety of rusting machine parts and two rectangular concrete cisterns. The southernmost cistern can be entered through a hole knocked in the south wall. A ladder also runs up to the roof.
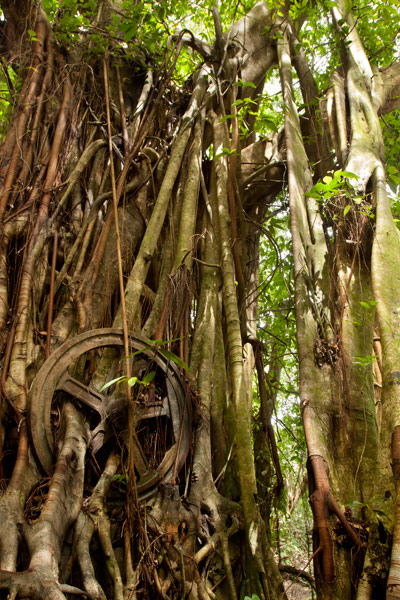

“The Banyan Wheel” (Dausong)
The most photogenic of the island’s attractions is not far from the main path on a terrace cut into the eastern slope of Dolen Lenger. There are several concrete foundations here and on one of them is an unidentified machine (perhaps an engine or rock-crusher) that has been completely absorbed by a huge banyan tree, such that the large machine wheel is permanently fixed on the outside of the tree with two roots growing right through the spokes. Take our word for it: it’s pretty darn cool.
Northeast Side
Seaplane Hangar & Aircraft Wreckage (Dietakai)
The hangar on the northeast side of the island once housed the “flying boats” that flew between Chuuk, Pohnpei, and the Marshall Islands and the Naval Type-O Observation seaplanes that were used for recon.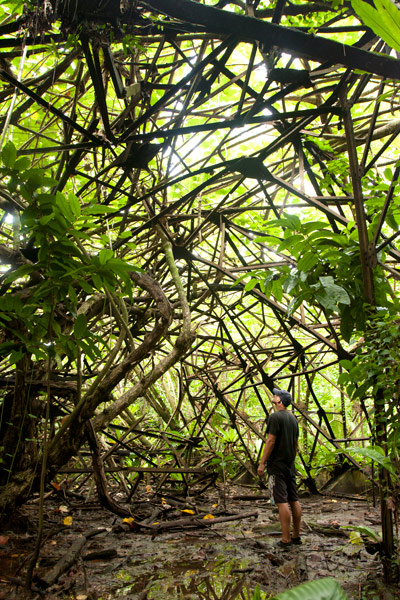  The structure sustained at least two direct hits from bombs, leaving massive craters at the front and on the southeast wall and possibly contributing to the eventual collapse of most of the braced girder roof in the 1980s (only the rear portion still stands). Near the northeast corner is a half-buried air compressor and just beyond this the engine cylinder of a destroyed aircraft, but the tangled girders make it difficult to move further inside from this direction. A careful search near the east side of the foundation should yield the wreckage of at least one plane (an Aichi E13A1 Jake), including the engine and propeller, portions of a wing, a pontoon, strut, and bits of bulkhead next to one of the carriers used to move the planes. The hangar can be much more easily entered at the rear, where the roof girders are still intact. A pair of carriers — on their way to being devoured by a ficus — were used to transport the seaplanes.
The structure sustained at least two direct hits from bombs, leaving massive craters at the front and on the southeast wall and possibly contributing to the eventual collapse of most of the braced girder roof in the 1980s (only the rear portion still stands). Near the northeast corner is a half-buried air compressor and just beyond this the engine cylinder of a destroyed aircraft, but the tangled girders make it difficult to move further inside from this direction. A careful search near the east side of the foundation should yield the wreckage of at least one plane (an Aichi E13A1 Jake), including the engine and propeller, portions of a wing, a pontoon, strut, and bits of bulkhead next to one of the carriers used to move the planes. The hangar can be much more easily entered at the rear, where the roof girders are still intact. A pair of carriers — on their way to being devoured by a ficus — were used to transport the seaplanes.
Seaplane Ramp & Apron (Dietakai)
The large seaplane ramp and apron dates to 1939 or shortly after and was constructed by a labor force consisting of Japanese, Korean, Pingelapese, Mwoakillese, and Pohnpeian workers. The structure lies on a reclaimed portion of the island and stretches northeast into the sea. The underwater section was made from concrete slabs poured elsewhere and lowered from barges, where they were assembled by divers. Stone seawalls around the perimeter were constructed in the highly stable yabane-tanizumi configuration. Written accounts left by local workers describe slave-labor conditions and harsh punishments for anyone who did not cooperate (one account says men were strung up to bake in the sun). A Pohnpeian marching dance (“Ke Dehr Lemeleme Me Se Ruksang Doadoahk en Kaigun”) composed during the event, commemorates the regular desertions of laborers.
Today, the cratered apron has been claimed by the forest and is difficult to even identify from the ground, but at the time of writing there was a clear path across it. The ramp was repaired by the Americans and used as the primary airstrip until the current airport on Dekehtik was completed. It remains mostly intact, though several structures in the area post-date the Japanese period (including an old hut for picnickers and the concrete tanks from a giant clam hatchery that operated in the 1990s).
Dolen Lenger

Dug-Outs & Tunnels (Dolen Lenger)
The ascent of Dolen Lenger follows the northernmost of two Japanese roads that lead up the hill and eventually intersect. The lower part of the southern road is mostly blocked by trees and mud and is no longer a good way to access the hill, but you can explore the upper section, where several dug-outs cut into the slope on either side. Two of the entrances are connected by a short tunnel.
Gatepost & Barracks Foundations (Dolen Lenger)
A bit further up the northern path, hikers pass a gatepost (its twin has fallen down the hill), adorned with round, colorful river stones imported from Japan. Naval personnel gathered at this spot for their morning meeting. Not far ahead, the foundations of a barracks complex are found on a large terrace in the hillside. The area is littered with Japanese beer bottles, old diesel engines, steel water tanks, and rusting machine parts. A short tunnel worms into the slope to the left of where the path climbs a flight of concrete steps and continues up the hill.
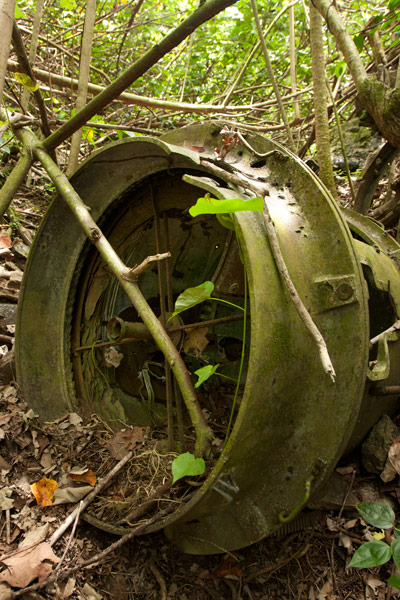

Searchlight (Dolen Lenger)
The drum and turn-table of a 110 cm searchlight (probably a Navy Model 92) lie just off the right edge of the path. The light was originally mounted on the rock outcropping five meters (16 ft) west of the its current position and was used to identify targets at night. It was probably dismantled by American personnel after the war.
Small Gun Station (Dolen Lenger)
Further along, a deviation from the main path leads to an unknown battery, probably for a machine gun or small artillery, which was removed after the war. A short stone wall protects the site and contains two ammunition magazines.
Anti-Aircraft Gun Stations (Dolen Lenger)
Two anti-aircraft batteries crown the hill, one to the west and the other at the end of the main path. Both sites consist of concrete rings surrounded by stone and earth revetments and a number of ammunition magazines (nine at the first station and six at the second). Naval 8 cm Type 3 Dual-Purpose Guns were installed at these locations to protect the seaplane base and other important Lenger facilities. Unfortunately, both guns were removed after the war.
Dolen Lenger Summit Area
From the last anti-aircraft gun station, it’s possible to continue another 50 meters (164 ft) or so to the 77 meter summit of the hill (marked with a brass USGS benchmark) and pick your way to the cliff-top for expansive views of Kolonia and the northern lagoon. Bring a machete and take care at the edge of the precipice.
Coastal Battery & 15 cm Naval Gun (Dolen Lenger)
Just north of the searchlight, a branch in the path turns west and descends a series of muddy steps to the coastal batteries and their four naval gun stations. Records disagree as to whether guns were actually installed at all four of the stations or if one station at each battery was a decoy. The only gun remaining on Lenger — a 15 cm 40 caliber British Armstrong-Whitworth naval canon — lies on its side in the mud at the southernmost station not far from the pedestal mount. It was probably thrown there by the detonation of one of the many bombs dropped by Allied aircraft in 1944. The barrel and shield are separated from the jacket and recuperator and partly buried. Japanese records state that the 15 cm gun on Sokehs Mountain was originally installed at Lenger and moved during the war. Lenger’s guns were intended to prevent surface invasions from Pweitik Passage to the northwest and had a range of roughly 7 kilometers (4.3 mi).
Heavy Ordnance Magazine Foundation (Dolen Lenger)
Past the gun stations is the foundation of what was probably a magazine for heavy ordnance surrounded by impressive inclined blast walls of quarried basalt rock. As is true of the best examples of Japanese architecture on Pohnpei, the stones were laid in the alternating diagonal pattern called “herringbone style” (or yabane-tanizumi). The site was most definitely covered during the operational period and camouflaged to make it invisible from the air.
West Side
Coastal Barracks Foundations
The remains of two large barracks are found on the western coast of the island. Both of the structures were wooden pitched-roof buildings raised above the ground on concrete posts and reached by short flights of stairs. Each barracks housed as many as fifty men. Only the posts and stairs remain today. The southern foundation has a nahs built on top of it, which was part of one the island’s two “resorts” in the 1990s.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The Lenger Island guide would not exist without the amazing work and cooperation of archaeologist Takuya Nagaoka, who was the first person to map the historical sites on Lenger. Nagaoka’s meticulous survey maps and exhaustive report (as yet, unpublished) were indispensable in the process of finding and interpreting neglected sites that had become heavily overgrown.
Eco-Adventure Map Guides >> Lenger Island >> Lenger Historical Sites