Nan Madol Ruins









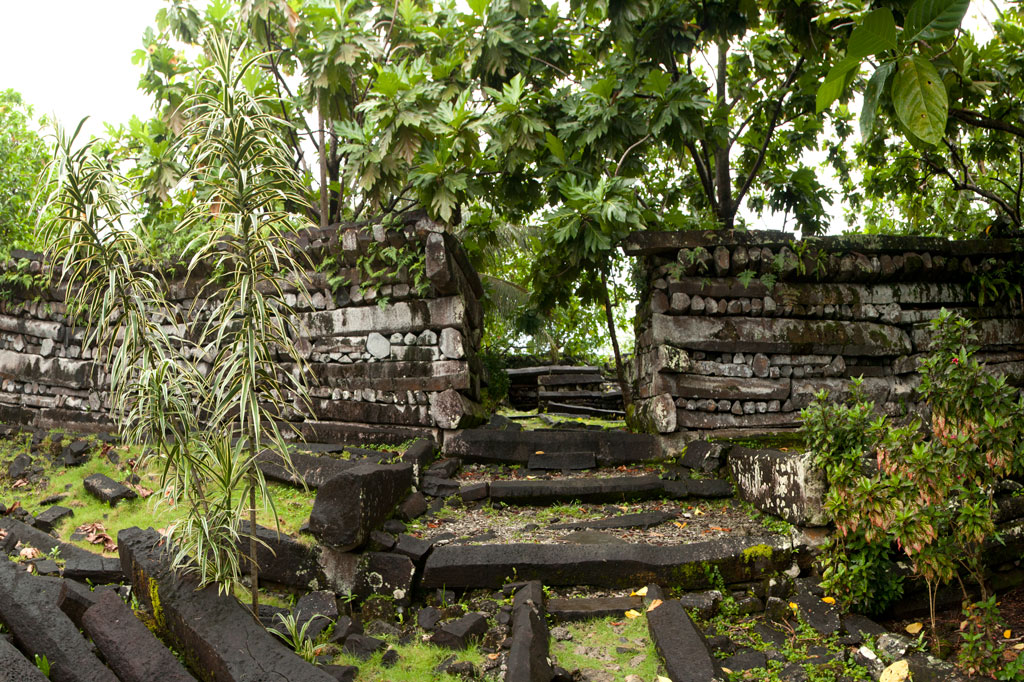
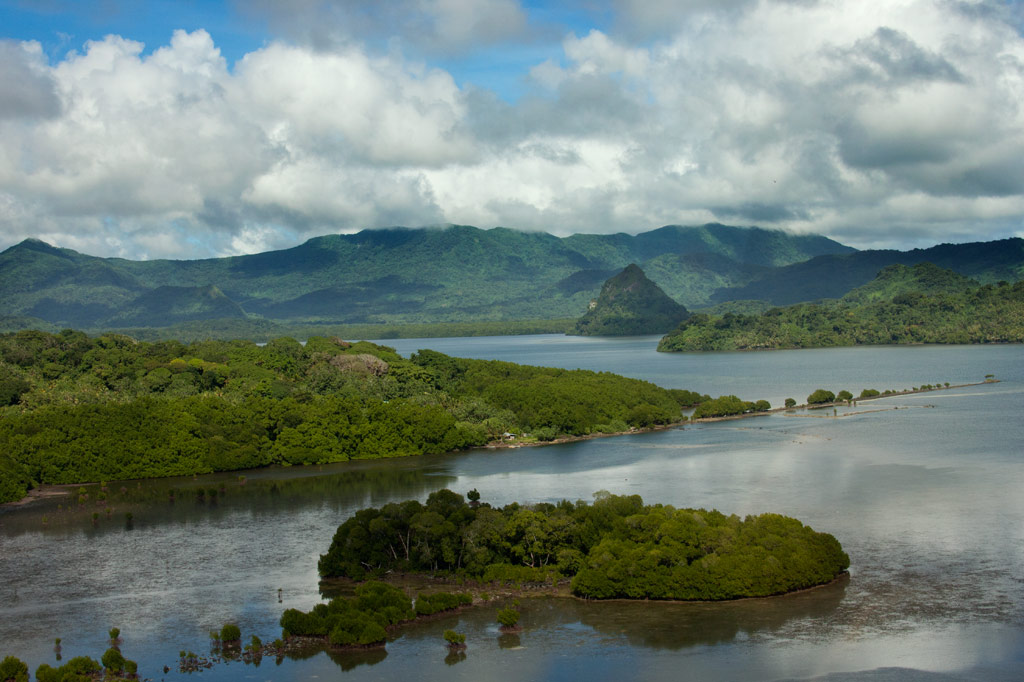
Nan Madol is a prehistoric “city” of more than ninety man-made islets off the coast of Temwen Island, constructed of naturally-occurring prismatic basalt columns, basalt boulders, and coral fill. Many of the islets have large, complicated structures on them composed of the same types of rock — stones as heavy as 90 tons. Together, the islets formed a powerful administrative and religious complex from which the island of Pohnpei was ruled for several hundred years by a line of tyrannical monarchs called Saudeleurs. The lower city, Madol Pah, was the administrative center, while the upper city, Madol Powe, was the ceremonial heart of the complex.
Megalithic sites like Nan Madol are rare around the world and even rarer in the Pacific. Anyone who has seen the city would place it alongside other more famous megalithic feats such as the pyramids of Egypt and Central America, Stonehenge, Machu Picchu, and Rapa Nui’s moai. And yet, Nan Madol is little-known outside the archaeological community and visited by a surprisingly small number of people each year. Nan Madol was inscribed onto the UNESCO World Heritage List in July 2016.
Archaeological Work at Nan Madol
Archaeological investigation of the ruins began during the German Period in the late 1800s. German anthropologist Paul Hambruch created the first map of Nan Madol in 1910, which is often still used today. During the Japanese Period (1914-1945), three different archaeologists — Hasebe, Yawata, and Muranushi — conducted surveys and excavations. Sporadic field research has been on-going ever since with Japanese and American archaeologists (Saxe, Allenson, Loughridge, Ayres, Haun, Bath, Athens, Mauricio, Kataoka, and Nagaoka) doing the bulk of the work. Masao Hadley, Rufino Mauricio, and Pensile Lawrence were instrumental in piecing together the oral history relating to the site. Little of the archaeological findings, however, have made their way to the general public, and there is a great deal of unpublished material that has never been released in any form — to the great detriment of the historical preservation effort.
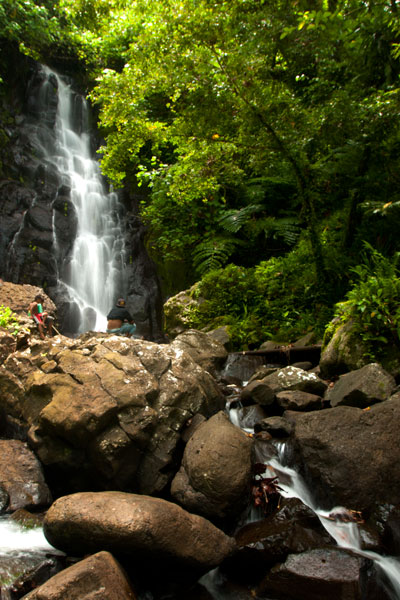
About 30 of the islets have been meticulously surveyed and mapped to date. Even so, there remains much to be learned about the ruins. Those reluctant to accept the mythical explanation of the city’s origin have theorized wildly about how such an engineering feat could be achieved. The basalt columns at Nan Douwas are as heavy as 5 tons and are stacked log cabin-style to form walls has high as 7.5 meters (25 ft), while boulders weighing as much as 90 tons are piled to heights of 8 meters (26 ft) at Pahnwi. Though it is plausible that stones might have been hoisted into place with the help of ropes, levers, earth ramps, and mass man-power, the real question that has bothered everyone (except Pohnpeians) is how the stones got to Temwen Island at all. Most of the quarry sites are nowhere near Nan Madol; in some cases they are on the other side of Pohnpei. How did the builders transport the columns over such distances? The foremost theory proposes that the stones were floated on rafts through the lagoon, but as the process has not been successfully demonstrated, the mechanics of Nan Madol’s construction will likely puzzle scholars and amateurs alike for years to come.
Kahnimweiso — the Sunken City
The eerie blue deeps between Madol Powe (the upper city) and Nahkapw Island are known as Pahn Nahkapw — “below Nahkapw” — and are believed by some to be the resting place of an ancient city called Kahnimweiso. In the late 1970s, archaeologist Arthur Saxe was told of the city Olsihpa and Olsohpa saw from a mountaintop prior to building Nan Madol and was intrigued. If Kahnimweiso had existed at all, Saxe wanted to know how it could possibly end up on the bottom of a reef passage.
Saxe noted that some aspects of Pahn Nakapw were unusual. At first glance it appears to be a pass, and yet it has no outlet; in the north, the deep water terminates just beyond Na Island. Saxe postulated that Pahn Nahkapw could be a “blue hole” — a collapsed section of fringing reef — rather than a true channel. According to his theory, freshwater run-off from Temwen seeped down beneath the reef and dissolved sections of it over a long period of time, forming passages and caverns. The weight of the basalt used to build Kahnimweiso eventually caused a cataclysmic collapse of the reef shelf and sent the city to the depths.
Diving due east of Kerian, Saxe discovered a line of “pillars” on the seafloor, which he thought might be part of the fabled gate to Kahnimweiso. Disappointingly, the pillars were later proven to be natural coral formations rather than basalt columns. No serious underwater exploration has been done since, and yet the mystery continues to fascinate. A Japanese archaeologist took bathyspheric measurements at Pahn Nahkapw in 2012 and determined that the deepest area is about 65 meters (213 ft). Do the remains of a city really lie under the water? Additional research is needed to answer the question definitively.
A History of Nan Madol
The story of Nan Madol began around 900 A.D. with the arrival of two mysterious brothers named Olsihpa and Olsohpa. Oral history states that this pair came from Katau Peidi, an unknown island in the West (who some claim is Yap). Whether they were sorcerers or holy men is a matter of debate, but there was something extraordinary about these men. Until that time, Pohnpei had never had a unified political structure, but that was exactly what Olsihpa and Olsohpa wished to create. They landed first at Soupaip (an ancient name for Sokehs Island), built some stone structures in Ipwal, and then departed because the local inhabitants seemed hostile to outsiders. Next they stopped at a point on the coast of Tipwendongalap (in what is now Nett), but the currents and waves there were too strong for building. The third stop was on the northern coast of Takaieu Island in Wenik Peidak (now U) and the fourth at Likin en Mwahn near present-day Alohkapw, Madolenihmw. But neither of these locations was acceptable. Climbing a nearby mountain (Pohn Tehnmei), the brothers looked down for the first time on the panorama of Sounahleng — the “reef of heaven” — in the area around Temwen Island. They saw something there, but it’s not clear what; either a vision of what was to come or the actual ruins of a city originating even further back in Pohnpei’s ancient past (some of the less elaborate stone structures at Nan Madol may have been built as early as 500 A.D.). Whatever the case, Sounahleng was perfect.
Using their supernatural abilities, the brothers flew huge boulders and prismatic basalt columns from all over Pohnpei and assembled them into a 1 km2 (200-acre) capital city with more than ninety artificial islets connected by shallow canals. They named the region Deleur and the city Nan Madol after the spaces between the islets. After Olsihpa’s death, Olsohpa declared himself Saudeleur, “Lord of Deleur”, supreme ruler of all Pohnpei. He was the first ruler in a dynasty that lasted perhaps as long as 500 years.
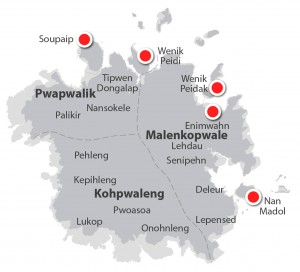
Under the Saudeleurs, Pohnpei was divided into three parts. Malenkopwale consisted of what is now Madolenihmw and U, Pwapwalik was made up of the areas now called Sokehs and Nett, while Kohpwaleng roughly coincides with modern Kitti. Olsohpa and the Saudeleurs that followed him were completely supported by forced tribute from the Pohnpeian people with tribute events following the harvest seasons of important island staples, such as breadfruit and yams. The Saudeleurs brought the people under their control by giving titles to the leaders of the various semi-autonomous regions around Pohnpei. Each title came with specific obligations toward Nan Madol. The Saudeleurs also attempted to impose their religion — centered around the worship of the god Nahnisohnsapw — on the populace. Every year, a special ceremony of atonement was held at Idehd islet, where a turtle was sacrificed to a sacred eel. If the eel accepted the offering, Nahnisohnsapw was pleased with the people.
As time progressed, the Lords of Deleur became more and more tyrannical. One of them required tribute for every single thing a person possessed, including the lice on his or her body. Another Saudeleur had a hankering for human flesh and made sure the fattest Pohnpeians ended up as his dinner. A fearsome dog, Ounmatakai, kept an eye on the people and reported anyone who broke laws or failed to fulfill his or her duties. Violators were brutally punished at the Saudeleur‘s residence, Pahn Kadira, and sometimes executed afterward at an islet across the canal that came to be known by the ominous moniker Wasao — “that place.”
Unrest began to spread. The boldest regions of the island, including Palikir and Kepihleng (areas in what are now Sokehs and Kitti), began to defy the authority of Nan Madol. When the Saudeleur tried to bolster the influence of the Nahnisohnsapw religion, the region of Salapwuk (which had its own religious cult devoted to Nahnsapwe — the thunder god), rebelled. This event was the beginning of the end for the Saudeleurs. Threatened by Salapwuk‘s defiance and competing religion, the Saudeleur imprisoned their god, Nahnsapwe, at Pahn Kadira. Nahnsapwe, however, escaped and fled to an island in the East, which some say was Kosrae. There he impregnated a mortal woman, who bore a son named Isokelekel.
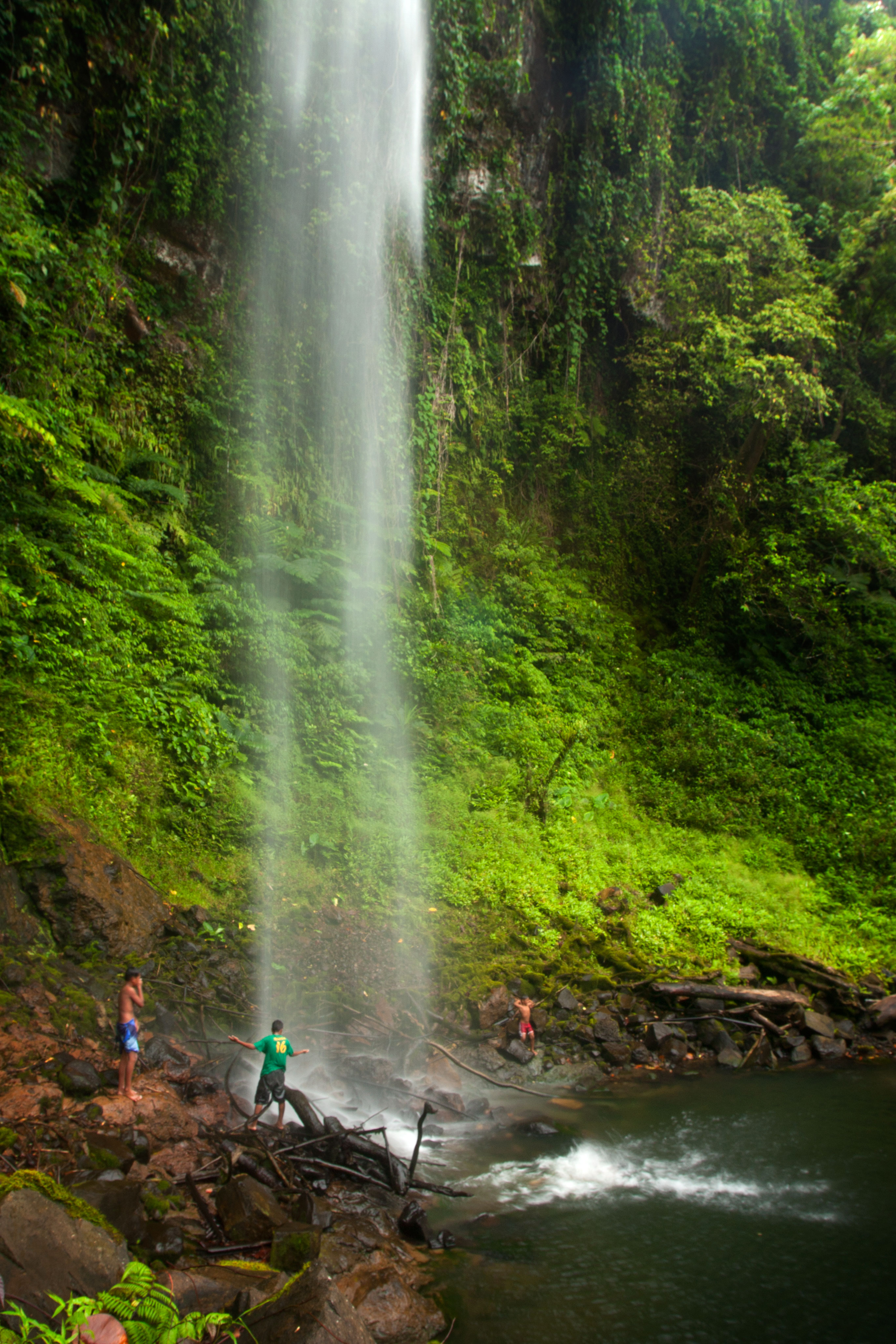
As Isokelekel grew up, he learned the story of the Saudeleur and vowed to avenge his father. When he became a man, he trained 333 warriors and set sail for Pohnpei. He landed first at And Atoll, 15 km southwest of Pohnpei, and dwelt there for some time, learning about the island from the atoll’s residents and acquiring a wife. He then took his canoes, passed through Kehpara Pass (Dauen Kehpara), and sailed clockwise around the island toward Nan Madol. The Saudeleur was initially suspicious of the newcomers, but as they showed no obvious signs of aggression, he invited them to stay at the islet of Kelepwel. They lived there for some time, marrying Pohnpeian women and fathering children. Eventually, however, some small disagreement blossomed into open war. After several days of bitter fighting, the Saudeleur‘s men gained the upper hand and it seemed as though Isokelekel would be defeated. At that moment, one of his fiercest warriors, Nahnesen, rallied the fighters, spearing his own foot to the ground to show that retreat was not an option. The tide turned, and Isokelekel’s men chased the Saudeleur‘s army all the way to Sapwalap. The final battle was fought at a waterfall called Kamau Pwoungapwoung. There the last Saudeleur was utterly defeated and transformed into a small blue fish that resides in that pool to this day.
After the battle, Isokelekel was given the title Nahnmwarki and became the first paramount chief. His domain — the eastern part of Pohnpei — was renamed Madolenihmw, which means “separation between the houses.” Isokelekel and his descendants continued to live at Nan Madol until the early 1800s when the city was finally abandoned and left to the wind, the water, and the trees. No one is certain why the Nahnmwarki deserted Nan Madol, but a likely possibility was that living on the artificial coral islets, where little could be grown or produced, just wasn’t practical any longer. While fear had motivated the Pohnpeian people to provide the Saudeleurs with everything they needed to live at Nan Madol, their relationship with the paramount chiefs was different and the Nahnmwarki had to be more self-reliant. Others have postulated that an epidemic, a natural disaster, or the arrival of Westerners led to the abandonment of Nan Madol.
Featured Islets
Today much of Nan Madol has been swallowed by the mangroves and is further threatened by the strangling power of tree roots; the action of wind, rain, and waves; and the impact of both local residents and visitors. About a third of the islets can still be visited. We’ve featured eight here that absolutely should not be missed.
Dorong
Dorong (tō.rōng) is most notable for its central feature, Lehnkei, a natural reef pool around which the islet was constructed. A type of clam (Anadara sp.), called lipwei in the Pohnpeian language, was raised in the pool and harvested during special ceremonies. Men baited the clams with coconut fronds and then dove down and collected them. Lehnkei was connected to the lagoon by eleven ingeniously-engineered channels that ran under the coral fill of Dorong to the ocean, allowing the pool water to circulate. One of the channels near the southeast wall of the 9,792 sq. meter islet held a sacred eel, referred to as saleng iahia (“rainbow ear”). Many informants have also claimed that there was a tunnel opening at the bottom of Lehnkei that led to a place “beyond the reef.” It was said that a stick thrown into the pool would surface far away. Some insisted this place was in the open ocean beyond Nahkapw Island, while others said the tunnel connected Lehnkei with another pool next to Lemenkau islet, called Namwenkau. The second theory seems the most plausible, but so far no one has found any hard evidence that the tunnel actually exists, however intriguing the idea may be. In addition to the pool, Dorong has many stone house platforms and the foundation of a large U-shaped meeting hut (nahs) with three large sakau stones (peitehl), one of which weighs two tons.
Dorong is now almost completely surrounded by mangroves. The only way to visit the islet is by kayak, canoe, or paddleboard. Access is easiest at the north corner, which happens to be the tallest and most elaborate part of the perimeter wall. From there, it’s possible to follow the wall and then cut into the interior to view the pool and other major features.

Idehd
Idehd (ee.tĕht) was built around 1200 A.D. and served as the religious center of Nan Madol from 1260 to 1380 A.D. Sea turtles were sacrificed annually by the high priests and fed to a moray eel (Nan Samwohl) found in a small hole near the northeast entrance of the 1,310 sq. meter islet. The eel’s acceptance of the offering indicated that the people were in the favor of the powerful god of the Saudeleurs, Nahnisohnsapw. The most interesting features of Idehd include a walled enclosure at the east corner around Nan Samwohl’s hole; 333 sling-stones brought by Isokelekel’s warriors; and a 2.5-meter-tall midden formed by centuries of food waste.
Idehd is best visited by kayak or canoe, as the primary canal has become silted-in and is too shallow for a full-sized boat, except at the highest of tides. The walls are in bad shape with major collapses in several places. The northwest edge of the islet is partially submerged in the canal (this is the easiest access point). Basalt columns from various spots on the islet were collected and moved in modern times to form the walkway entering the site. The islet is surrounded by mangroves on three sides.
Kerian
Kerian (kĕr.ee.än), a 1,150 sq. meter tomb for the high priests, comes closest of all the islets to the grandeur of Nan Douwas. High perimeter walls were intended to protect the site from the angry waves that characterize the deep water beyond the east corner, but time has taken its toll and the outer part of the north wall is slowly collapsing. Three burial chambers are found inside the enclosure, which can be entered through a low gate on the southwest wall, and the sakau stone near the entrance is 2 meters long. Stories say that a particular flowering shrub (Ixora casei) grew on the island and was used to make spears.
Because the water is often rough around the north corner of the islet, it’s best to approach Kerian from the west and dock on the protected side.

Lemenkau
Lemenkau (lĕm.ĕn.käū), on the eastern perimeter, functioned as the center of local medicine and healing. It was positioned to incorporate the 6-meter-deep reef pool, Namwenkau, that lies off the southwest wall. After treatment, patients bathed in the pool to wash away any lingering traces of black magic before returning home. Lemenkau has a house foundation and three tombs and is littered with dozens of large sakau pounding stones called peitehl.
The easiest place to enter is at the northwest corner. The islet has much less vegetation than most of Nan Madol‘s islands, and yet it is still a tough place to explore — barren, hot, and very rough on the feet.

Nan Douwas
Nan Douwas (nän tō.wäs) — certainly the visual heart of Nan Madol — is a grand mortuary complex and temple for the Saudeleurs built sometime around 1200 A.D. The name in the honorific language means “in the mouth” and implicitly references the mouth of the chief. The 3,400 sq. meter islet is roughly square with two walled enclosures, one inside the other. The outer perimeter walls, constructed of huge prismatic basalt columns, are impressive, reaching heights of up to 7.5 meters. At the corners, the walls project outward, intensifying the feeling of one’s relative smallness. Inside the first courtyard are two lesser tombs, one on the north side and one on the south. A small rectangular pit at the rear of the courtyard is claimed by some informants to be the place where prisoners were kept. The walls of the second enclosure are smaller. The primary feature is the great central tomb, which originally contained the bones of Saudeleurs and Nahnmwarki (it was excavated by archaeologists in both the German and Japanese Periods and all bones were removed). Also on the islet are several huge peitehl, and three passages beneath the walls.
Nan Douwas is the only site in the ruins that is consistently maintained and has a park-like atmosphere. Even so, tree roots, the elements, and the sheer weight of the rocks (called deadloading) have taken their toll; six major collapses have occurred — the most devastating on the outer perimeter wall, north of the entrance. Archaeologists have also identified cracks in the gigantic boulder that serves as the keystone of the southeast corner. If this stone was to split apart, the results would be disastrous. Well-tended paths run around all of the major features on the islet including the outer perimeter.
Pahn Kadira
Pahn Kadira (pähn kät.ee.rä) is one of the largest islets in the ruins — 12,770 sq. meters including the annex — and had three phases of construction, the first between 950 and 980 A.D., the second from 1250 to 1290 A.D., and the last from 1460 to 1480 A.D. The islet served as the Saudeleur’s residence and administrative headquarters with the Temple of Nankieilmwahu — dedicated to the thunder god — at its center. The four corners of the islet were constructed by master builders from Malenkopwale (now Madolenihmw), Kohpwaleng (now Kitti), Pwapwalik (now Sokehs) and Katau Peidak — believed to be Kosrae. It was said that if one of these corners collapsed, the state associated it with it would also come to harm (the Sokehs corner allegedly fell just before the defeat of the Sokehs people in the Rebellion of 1910, and the Kosrae corner crumbled before a major small pox epidemic that killed all but about 800 Kosraeans).
The Saudeleur’s living quarters were located at the rear of the islet and had walls as high as 5 meters, though they are now partially collapsed. The open area northeast of the residence was used for growing taro and sugar cane. A residential enclosure for the Saudeleur‘s guards is found at the south corner. Canoes were docked at the intersection of the southeast wall of the annex and the southwest wall of the primary islet. The enclosure at the east corner was the Saudeleur’s bathing complex. Finally, the annex was where the Saudeleur‘s many wives lived. The Smithsonian Institute conducted surface surveys on Pahn Kadira and collected a large number of small artifacts, including fish hooks, beads, and spondylus shell ornaments. The site is best accessed from the southeast wall adjacent to the main canal.
Pahnwi
Pahnwi (pähn.wee), built around 1250 A.D., forms the southwest corner of Madol Pah and was the place visitors docked their canoes. The name means “under the sea poison tree,” a reference to a Barringtonian asiatica tree that grew up in the area. Though the 7,700 sq. meter islet has three house foundations, two stone tombs, and several other burial sites, they are now largely inaccessible due to its overgrown state. Archaeological excavations uncovered a massive collection of artifacts, including shell fishing lures, conus ring arm bands, beads, and an intact cranium. The most striking feature is the outer wall, where Nan Madol’s largest boulders (some estimated at 90 tons) have been piled to a height of 8 meters. In ancient times, pregnant women climbed to the top of Takain Ripkapehd, the “rock of the tightening stomach,” to ensure that their child would be blessed with good health.
Peinering
Peinering (pein.ĕ.reeng) was a manufacturing site for coconut oil used for ceremonial purposes, such as the anointing of the dead. Female workers stored the nuts, extracted and refined the oil, and oversaw distribution of the final product to the rest of the city. The islet, located in the middle of a sandy shoal, has walls as high as 3 meters and a well-preserved house foundation. Enter through the gap in the northwest wall.
Other Notable Sites
Dau
Dau (däū) is the last site that the Nan Madol trail crosses before coming to Nan Douwas. Archaeologists date the construction of this 5,100 sq. meter islet to between 1000 and 1250 A.D. Some of the soldiers, who guarded Nan Douwas, slept on Dau and sharpened their weapons (shell axes and spears) there. A sacred eel was also kept in a hole on the islet. Many coconut palms grow on Dau today, but unlike some of the other islets, Dau remains fairly free of underbrush and is easy to explore. There are six house foundations, a sakau stone, and canoe landing.
Kelepwel
Kelepwel (kĕl.ĕ.pwĕl), which means “walled soil,” lies across the canal from Pahn Kadira. The islet often served as the living quarters for the servants and guests of the Saudeleur. When the conqueror Isokelekel and his men arrived at Nan Madol, they were housed on Kelepwel while the Saudeleur tried to decide whether they were a threat to him. Artifacts dating to 1800s indicate that Westerners also resided on Kelepwel for a time. It is said that a traditional rock-throwing game was played on the islet. Kelepwel is currently heavily overgrown and cannot be easily explored.
Kepinehd
Kepinehd (kĕp.in.ĕht) is a relatively small islet on the southeast perimeter of the ruins. Oral history recounts how two women lived on Kepinehd and produced sails there, before they were finally banished and went to live with a community of ostracized women called liet. Kepinehd has three house foundations and two stone enclosures.
Kohnderek
Kohnderek (kōhn.tĕr.ĕk) is one of the northernmost islets of Madol Powe and dates to roughly 1400 A.D. When an important person died, the body of the deceased was perfumed on the 3300 sq. meter islet and prepared to be transported from islet to islet. A ceremonial dance called the “Dance of Death” was also performed and sakau was prepared to lighten the hearts of the friends and family of the deceased. Kohnderek is now thickly covered in trees and vegetation and the northeastern area is partially submerged. There are six house foundations on the islet.
Mweiden Nahnsapwe
Mweiden Nahnsapwe (mweit.ĕn nähn.säp.wĕ) is a small opening on the southeast perimeter between Kepinehd and Pikalap islets. The name means “passage of thunder.” After Nahnsapwe, the thunder god, escaped from his imprisonment by the last Saudeleur, he rested briefly at this place before making his way to Kosrae on the back of a magical needlefish.
Mweiden Weliwel
Mweiden Weliwel (mweit.ĕn wĕl.ee.wĕl) is an opening on the southeast perimeter between Pahnwi and Kepinehd islets. The name means “passage of the yellowfin tuna” and this was said to be the place where schools of tuna entered the city.
Nan Mwoluhsei
Nan Mwoluhsei (nän mwō.looh.sei) is a series of seawalls that protect the eastern side of Nan Douwas. The outer wall has only one entrance through which canoes could pass. The deep area to the east of the entrance was said to be the gate to a fabled city called Kahnimweiso that lies on the floor of Pahn Nakapw. Two sharks named Oun Mwoluhsei and Lioun Mwoluhsei allegedly guarded the area. Men threw pebbles into the sea to distract the sharks and demonstrated their courage by leaping from the wall into the water. If they survived the stunt, they were afforded great respect.
Pahn Douwas
Pahn Douwas (pähn tō.wäs), meaning “below the mouth (of the chief)”, is an islet immediately to the south of Nan Douwas, where guards and attendants slept. Pahn Douwas is currently quite barren, consisting primarily of rough coral fill that is extremely difficult to walk on. There are five house foundations here. The islet comes close to being submerged at high tide.
Pahn Mwasangapw
Pahn Mwasangapw (pähn mwä.säng.äp) is a burial vault on the eastern perimeter where low ranking priests were entombed. The site can be accessed from the ocean side.
Peikapw
Peikapw (pei.käp) is a large islet across the canal north of Pahn Kadira. Turtles, sacrificed on Idehd during an annual religious festival, were raised in the largest of four pools, called Namweias. This pool is also the place Isokelekel saw his reflection in is his old age, leading to his decision to commit suicide by self-castration. At a smaller pool, called Peirot, reflections on the surface of the water showed what was happening around Pohnpei and beyond, allowing the Saudeleurs to spy on their subjects. One story tells of two women who forgot to pay tribute to one of the gods and were transformed as punishment into two rocks found along the northeast wall of Peikapw.
Peikapw Sapwawas
Peikapw Sapwawas (pei.käp säp.wä.wäs) is a large islet south of Dau that was part of Nan Madol‘s communication system, along with Pwalahng and Usendau. At all three islets, triton trumpets and drums were sounded when announcements were made or news transmitted.
Pein Kitel
Pein Kitel (pein kee.chĕl) is a monumental burial complex (9,000 sq. meters) situated partly on the coast of Temwen and partly on the surrounding reef flats — the first structure encountered on the Nan Madol trail. Within the high perimeter walls are three smaller enclosures, each containing a burial vault. The vault near the southwestern corner is allegedly the tomb of Olsihpa and Olsohpa, Nan Madol‘s founders, and was excavated by German administrator Viktor Berg in 1907. Berg was said to have removed a collection of very large bones before dying mysteriously the following morning. The whereabouts of the bones are now unknown (if the story is true at all). The other two tombs held the remains of other Saudeleurs and the Nahnmwarki that followed them. Some local informants claim that the conquering hero Isokelekel was buried in the largest tomb.
Peinior
Peinior (pein.ee.yōr) is a small islet near the middle of Madol Powe, where women came to learn a sitting dance. There is little to see on Peinior now.
Peiniot
Peiniot (pein.ee.yōt) was originally intended as the place where food would be brought to be distributed to the people of the city. The location, however, was inconvenient — too far from the rest of the islets — and Pohn Douwas was used instead.
Pohn Douwas
Pohn Douwas (pōhn tō.wäs), located just north of Nan Douwas, was the one of the places where the guards and attendants of Nan Douwas slept. The name means “above the mouth (of the chief).” Food was also gathered on Pohn Douwas and jellyfish were baked in stone ovens. A well-maintained path runs along the length of the islet, which can be easily accessed from Nan Douwas.
Sapwutik
Sapwutik (sä.pwoo.chik) refers to a walled enclosure on the eastern perimeter, containing a tomb where priests were buried.
Usennamw
Usennamw (oos.ĕn.näm) was Nan Madol‘s primary kitchen — the place where food was gathered and prepared for the rulers.
Wasao
Wasao (wä.säū), which dates to about 600 A.D., was where people who displeased the Saudeleurs were executed after being tortured at Pahn Kadira. The small islet at the rear of Pahn Kadira developed such a dark reputation that people came to refer to it simply as wasao — “that place.” One of the Saudeleurs, a man called Raipwinloko, was a cannibal and was said to have disposed of human remains on Wasao after his grisly feasts. Archaeologists have found a great deal of pottery remnants on the island, indicating that Wasao was one of the older islets, occupied during the known period of pottery production.